Running phyloscanner in high-throughput on a population-based sample
Oliver Ratmann
2018-10-18
Source:vignettes/Rakai.02.run_phyloscanner.Rmd
Rakai.02.run_phyloscanner.RmdIntroduction
This tutorial describes the steps to infer phylogenetic relationships from a large number of deep-sequence phylogenies of individuals in the same potential transmission network. The main objective is to illustrate how large numbers of phyloscanner runs can be generated and run in parallel with the utility functions in this software package, without too much computational overhead.
The tutorial assumes that phyloscanner_make_trees.py was already run to generate read alignments and deep-sequence phylogenies for individuals in the same potential transmission network. For the demo analysis of data from the Rakai population-based sample of 2,652 infected individuals, these data are provided in Data Set S1.
Setting up the analysis
Start by extracting Dataset S1 from the command line, assuming that it was copied into a data folder called ‘RakaiPopSample_data’:
cd /Users/Oliver/sandbox/DeepSeqProjects
mkdir RakaiPopSample_deepseqtrees
tar -xvf RakaiPopSample_data/Dataset_S1.tar -C RakaiPopSample_deepseqtreesThe new directory should contain files that look as follows:
- Each analysis of a potential transmission network is identified with the prefix
ptyrX_whereXis an integer. Note that, to minimise computations, individuals in small transmission networks can be grouped into a single phyloscanner analysis, which we call a batch in this tutorial. In total, there are 345 batches. - Two files are available for each batch. First, a text file listing all individuals in the batch, in file
ptyrX_patients.txt. - Second, deep-sequence phylogenies of reads from individuals in the same batch, generated from overlapping read alignments across the genome, in file
ptyrX_trees_newick.zip. You can unzip the trees to see the coordinates of the genomic windows for which deep-sequence trees could be generated, but make sure you leave the zip files in the directory.
Next, open R and define the base directories for your project:
require(Phyloscanner.R.utilities)
HOME <- "/Users/Oliver/sandbox/DeepSeqProjects"
in.dir <- file.path(HOME, "RakaiPopSample_deepseqtrees")
out.dir <- file.path(HOME, "RakaiPopSample_phyloscanner_out")
work.dir <- file.path(HOME, "RakaiPopSample_phyloscanner_work")
prog.pty <- "/Users/Oliver/git/phylotypes/phyloscanner_make_trees.py"
dir.create(out.dir, showWarnings = FALSE)
dir.create(work.dir, showWarnings = FALSE)Here, prog.pty is the full path to the phyloscanner program phyloscanner_make_trees.py and work.dir is the name of temporary directory. Do make sure that the directory names above do not start with “~”, because the names are not expanded in the scripts below. White space, or characters like ‘-’ are OK.
Prepare bash scripts to run phyloscanner
The next step is to define the input arguments to phyloscanner. Please see the phyloscanner manual for details. The default arguments that were used for analysis of the Rakai population-based sample are as follows.
pty.args <- list( prog.pty=prog.pty,
prog.mafft=NA,
prog.raxml=NA,
data.dir=NA,
work.dir=work.dir,
out.dir=out.dir,
alignments.file=system.file(package="Phyloscanner.R.utilities", "HIV1_compendium_AD_B_CPX_v2.fasta"),
alignments.root='REF_CPX_AF460972',
alignments.pairwise.to='REF_B_K03455',
bl.normalising.reference.file=system.file(package="Phyloscanner.R.utilities", "data", "hiv.hxb2.norm.constants.rda"),
bl.normalising.reference.var='MEDIAN_PWD',
window.automatic= '',
merge.threshold=0,
min.read.count=1,
quality.trim.ends=23,
min.internal.quality=23,
merge.paired.reads=TRUE,
no.trees=FALSE,
dont.check.duplicates=FALSE,
dont.check.recombination=TRUE,
num.bootstraps=1,
all.bootstrap.trees=TRUE,
strip.max.len=350,
min.ureads.individual=NA,
win=c(800,9400,25,250),
keep.overhangs=FALSE,
use.blacklisters=c('ParsimonyBasedBlacklister','DownsampleReads'),
tip.regex='^(.*)_fq[0-9]+_read_([0-9]+)_count_([0-9]+)$',
roguesubtree.kParam=20,
roguesubtree.prop.threshold=0,
roguesubtree.read.threshold=20,
dwns.maxReadsPerPatient=50,
multifurcation.threshold=1e-5,
split.rule='s',
split.kParam=20,
split.proximityThreshold=0,
split.readCountsMatterOnZeroBranches=TRUE,
split.pruneBlacklist=FALSE,
trms.allowMultiTrans=TRUE,
pw.trmw.min.reads=30,
pw.trmw.min.tips=1,
pw.trmw.close.brl=0.025,
pw.trmw.distant.brl=0.05,
pw.prior.keff=2,
pw.prior.neff=3,
pw.prior.keff.dir=2,
pw.prior.neff.dir=3,
pw.prior.calibrated.prob=0.66,
mem.save=0,
verbose=TRUE,
select=NA
)
save(pty.args, file=file.path(out.dir, 'pty.args.rda'))Next, we will prepare UNIX bash scripts to run a large number of phyloscanner analyses on a population-based sample. Each bash script corresponds to the deep-sequence phylogenetic analysis of one batch of individuals that are analysed jointly.
For each batch of individuals to be processed, find the corresponding list of patients in the input directory:
pty.c <- data.table(FILE_PAT = list.files(in.dir, pattern = "_patients.txt",
full.names = TRUE))
pty.c[, `:=`(PTY_RUN, as.integer(gsub("ptyr", "", gsub("_patients.txt", "",
basename(FILE_PAT)))))]Check which (if any) batches have already been processed, and remove them from the TODO list:
tmp <- data.table(FILE_TRMW = list.files(out.dir, pattern = "_pairwise_relationships.rda",
full.names = TRUE))
tmp[, `:=`(PTY_RUN, as.integer(gsub("ptyr", "", gsub("_pairwise_relationships.rda",
"", basename(FILE_TRMW)))))]
pty.c <- merge(pty.c, tmp, by = "PTY_RUN", all.x = 1)
pty.c <- subset(pty.c, is.na(FILE_TRMW))For each batch of individuals, create a UNIX bash script to run phyloscanner:
setkey(pty.c, PTY_RUN)
pty.c <- pty.c[, {
prefix.infiles <- gsub("patients.txt", "", FILE_PAT)
cmd <- phsc.cmd.phyloscanner.one.resume(prefix.infiles, pty.args)
list(CMD = cmd)
}, by = "PTY_RUN"]Each bash script should look similar to this:
pty.c[1, cat(CMD)]CWD=$(pwd)
echo $CWD
mkdir -p "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41"
cp "/Users/Oliver/sandbox/DeepSeqProjects/RakaiPopSample_deepseqtrees/ptyr2_patients.txt" "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41"
unzip "/Users/Oliver/sandbox/DeepSeqProjects/RakaiPopSample_deepseqtrees/ptyr2_trees_fasta.zip" -d "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41"
unzip "/Users/Oliver/sandbox/DeepSeqProjects/RakaiPopSample_deepseqtrees/ptyr2_trees_newick.zip" -d "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41"
cd "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41"
Rscript /Users/Oliver/git/phylotypes/deprecated/NormalisationLookupWriter.R --scriptdir /Users/Oliver/git/phylotypes/deprecated "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_InWindow_" "/Users/Oliver/Library/R/3.3/library/Phyloscanner.R.utilities/data/hiv.hxb2.norm.constants.rda" "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_normconst.csv" "MEDIAN_PWD" --standardize
Rscript /Users/Oliver/git/phylotypes/tools/parsimony_based_blacklister.R 20 0 20 "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_InWindow_" "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_blacklistsank_InWindow" --dualsOutputFile "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_duallistsank_InWindow" --outgroupName REF_CPX_AF460972 --tipRegex "^(.*)_fq[0-9]+_read_([0-9]+)_count_([0-9]+)$" --multifurcationThreshold 1e-05 --branchLengthNormalisation "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_normconst.csv" --verbose
Rscript /Users/Oliver/git/phylotypes/tools/downsample_reads.R 50 $CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_ $CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_blacklistdwns_ --blacklist $CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_blacklistsank_InWindow_ --tipRegex "^(.*)_fq[0-9]+_read_([0-9]+)_count_([0-9]+)$" --seed 42 --verbose
Rscript /Users/Oliver/git/phylotypes/tools/split_hosts_to_subgraphs.R "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_" "ptyr2" --blacklist "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_blacklistdwns_" --outputdir "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41" --idFile "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_patients.txt" --outgroupName REF_CPX_AF460972 --splitsRule s --kParam 20 --proximityThreshold 0 --readCountsMatterOnZeroBranches --tipRegex "^(.*)_fq[0-9]+_read_([0-9]+)_count_([0-9]+)$" --multifurcationThreshold 1e-05 --branchLengthNormalisation "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_normconst.csv" --outputAsRDA --pdfwidth 30 --pdfrelheight 0.15 --verbose
Rscript /Users/Oliver/git/phylotypes/tools/classify_relationships.R "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ProcessedTree_s_ptyr2_" "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/subgraphs_s_ptyr2_" "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2" --branchLengthNormalisation "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_normconst.csv" --verbose
Rscript /Users/Oliver/git/phylotypes/tools/summary_statistics.R --scriptDir /Users/Oliver/git/phylotypes/tools "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_patients.txt" "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ProcessedTree_s_ptyr2_InWindow_" "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/subgraphs_s_ptyr2_InWindow_" "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_" --tipRegex "^(.*)_fq[0-9]+_read_([0-9]+)_count_([0-9]+)$" --blacklists "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_blacklistdwns_InWindow_" --verbose
Rscript /Users/Oliver/git/phylotypes/deprecated/TransmissionSummary.R "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_patients.txt" "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_classification_InWindow_" "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_trmStats.csv" --scriptdir /Users/Oliver/git/phylotypes/deprecated --summaryFile "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_patStatsFull.csv" --minThreshold 1 --detailedOutput "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_trmStatsPerWindow.rda" --allowMultiTrans --verbose
Rscript /Users/Oliver/Library/R/3.3/library/Phyloscanner.R.utilities/phsc.pairwise.relationships.Rscript --infile "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_trmStatsPerWindow.rda" --outfile "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_pairwise_relationships.rda" --trmw.min.reads 30 --trmw.min.tips 1 --trmw.close.brl 0.025 --trmw.distant.brl 0.05 --prior.keff 2 --prior.neff 3 --prior.keff.dir 2 --prior.neff.dir 3 --prior.calibrated.prob 0.66 --rel.likely.pair --rel.likely.pair.by.distance.only --rel.likely.pair.by.topology.only --rel.likely.pair.by.cross.table --rel.direction --rel.chain
Rscript /Users/Oliver/Library/R/3.3/library/Phyloscanner.R.utilities/phsc.read.processed.phyloscanner.output.in.directory.Rscript --prefix.infiles "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_" --save.file.base "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41/ptyr2_" --read.likelytransmissions --read.trees --read.subtrees --zip
mv ptyr2* "~/sandbox/DeepSeqProjects/RakaiPopSample_phyloscanner_out"
for file in *; do
zip -ur9XTj ptyr2_otherstuff.zip "$file"
done
mv ptyr2_otherstuff.zip "~/sandbox/DeepSeqProjects/RakaiPopSample_phyloscanner_out"
cd $CWD
rm -r "$CWD/pty_18-10-19-15-43-41" Run bash scripts (option 1)
Each bash script can be run from a UNIX terminal, we only have to write the scripts to file. This following code will write each script to the temp directory that you specified above, to a file named phsc.Wed_Oct_17_101858_2018.sh or similar:
invisible(pty.c[, {
outfile <- gsub(":", "", paste("phsc", paste(strsplit(date(), split = " ")[[1]],
collapse = "_", sep = ""), "sh", sep = "."))
outfile <- file.path(pty.args[["work.dir"]], outfile)
cat(CMD, file = outfile)
Sys.chmod(outfile, mode = "777")
Sys.sleep(1)
}, by = "PTY_RUN"])Each file can be run on a UNIX terminal, e.g.:
cd /Users/Oliver/Dropbox (SPH Imperial College)/2015_PANGEA_DualPairsFromFastQIVA/RakaiPopSample_phyloscanner_work
phsc.Wed_Oct_17_101858_2018.sh Run bash scripts (option 2)
Alternatively, the bash scripts can be processed on a high performance environment with a job scheduling system. We first define a PBS header for the job scheduling system, add the header to each script, and then submit each script to the job scheduling system. The exact form of the PBS header depends on your job scheduler, below is an example that works at Imperial.
hpc.load <- "module load R/3.3.3" # make R available
hpc.select <- 1 # number of nodes
hpc.nproc <- 1 # number of processors on node
hpc.walltime <- 15 # walltime
hpc.q <- "pqeelab" # PBS queue
hpc.mem <- "6gb" # RAM
pbshead <- "#!/bin/sh"
tmp <- paste("#PBS -l walltime=", hpc.walltime, ":59:59,pcput=", hpc.walltime,
":45:00", sep = "")
pbshead <- paste(pbshead, tmp, sep = "\n")
tmp <- paste("#PBS -l select=", hpc.select, ":ncpus=", hpc.nproc, ":mem=", hpc.mem,
sep = "")
pbshead <- paste(pbshead, tmp, sep = "\n")
pbshead <- paste(pbshead, "#PBS -j oe", sep = "\n")
pbshead <- paste(pbshead, paste("#PBS -q", hpc.q), sep = "\n")
pbshead <- paste(pbshead, hpc.load, sep = "\n")Our header thus looks as follows:
#!/bin/sh
#PBS -l walltime=15:59:59,pcput=15:45:00
#PBS -l select=1:ncpus=1:mem=6gb
#PBS -j oe
#PBS -q pqeelab
module load R/3.3.3We are now ready to add the header to each script, and submit the job:
invisible(pty.c[, {
cmd <- paste(pbshead, "cd $TMPDIR", sep = "\n")
cmd <- paste(cmd, CMD, sep = "\n")
outfile <- gsub(":", "", paste("phsc", paste(strsplit(date(), split = " ")[[1]],
collapse = "_", sep = ""), "sh", sep = "."))
outfile <- file.path(pty.args[["work.dir"]], outfile)
cat(CMD, file = outfile)
cmd <- paste("qsub", outfile)
cat(cmd)
cat(system(cmd, intern = TRUE))
Sys.sleep(1)
}, by = "PTY_RUN"])Expected phyloscanner output
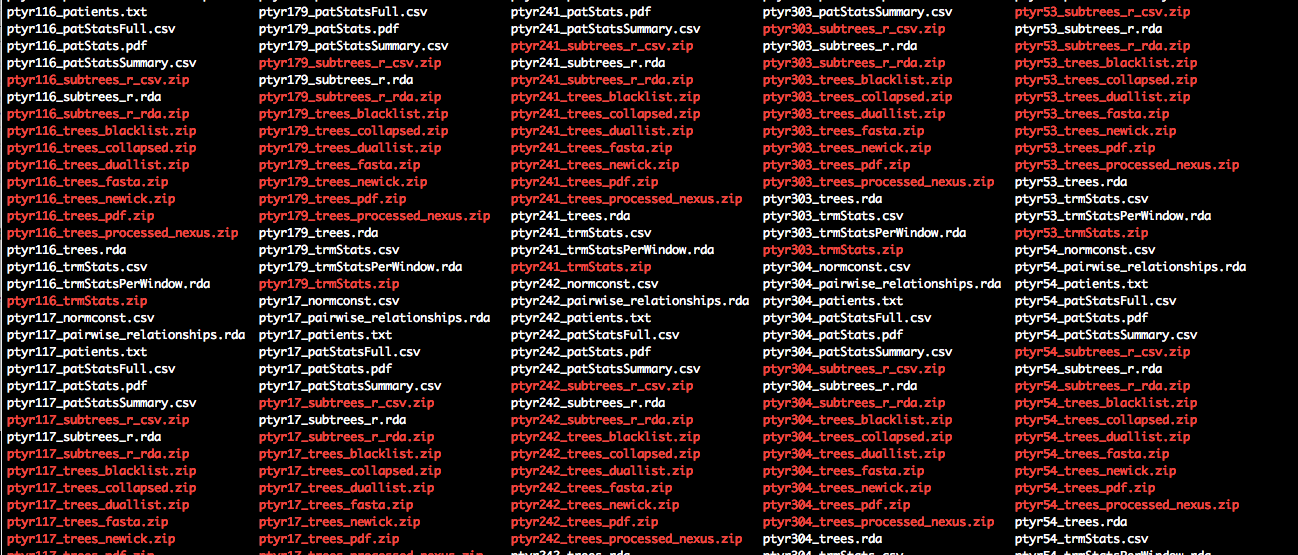
Once all scripts are run, the output directory contains for each batch a number of files, of which the files called ptyrX_pairwise_relationships.rda are used for reconstructing HIV-1 transmission networks from the population-based sample.
Below is a description of the full output.
-
ptyrX_patients.txtInput file, list of individuals in this batch. -
ptyrX_trees_newick.zipInput file, deep sequence trees. -
ptyrX_pairwise_relationships.rdaMain output file for reconstructing HIV-1 transmission networks.
-
ptyrX_normconst.csvFile containing multipliers used to standardise branch lengths of each deep-sequence phylogeny. -
ptyrX_trees.rdaDeep-sequence phylogenies in ape format, annotated with subgraphs of each individual. -
ptyrX_trees_processed_nexus.zipDeep-sequence phylogenies in nexus format, annotated with subgraphs of each individual. -
ptyrX_trees_collapsed.zipCollaposed deep-sequence phylogenies, with all blacklisted taxa removed. -
ptyrX_trees_pdf.zipPDFs of the deep-sequence phylogenies. -
ptyrX_patStatsFull.csvDetailed description of subgraphs of all individuals in this batch across the genome. -
ptyrX_patStatsSummary.csvSummary description of subgraphs of all individuals in this batch across the genome. -
ptyrX_patStats.pdfPDFs visualising properties of the subgraphs of all individuals in this batch across the genome. -
ptyrX_trmStats.zipDetailed description of pairwise phylogenetic relationships of all individuals in this batch across the genome, in csv format. -
ptyrX_trmStatsPerWindow.rdaDetailed description of pairwise phylogenetic relationships of all individuals in this batch across the genome, in R format. -
ptyrX_trmStats.csvSummary description of pairwise phylogenetic relationships of all individuals in this batch across the genome. -
ptyrX_subtrees_r_csv.zipDetailed description of subgraphs of all individuals in this batch across the genome, in csv format. -
ptyrX_subtrees_r_rda.zipDetailed description of subgraphs of all individuals in this batch across the genome, in R format.
-
ptyrX_trees_blacklist.zipNames of blacklisted taxa of all individuals in this batch. -
ptyrX_trees_duallist.zipNames of potential contaminants of all individuals in this batch.